Summary / TL;DR
Image optimisation improves website performance by reducing image file sizes without sacrificing quality, which enhances load speed, SEO rankings, and user experience. Compressing images allows pages to load in under two seconds, which reduces bounce rates and increases conversion rates, especially for mobile users. Techniques include using lossy or lossless compression, choosing efficient file formats like WebP or AVIF, renaming files for search visibility, and adding descriptive alt text. Tools such as Photoshop or WordPress plugins automate these tasks. Although time-consuming, image optimisation is crucial for high-performing, mobile-friendly websites that rank well and engage users effectively.
It’s no secret that one of the most common problems seen on web pages is a slow load time.
As the internet grows more image-heavy, it’s evident that you cannot just make a text-only page to pull in your target audience. On the other hand, no one likes to wait for a web page to open. As a result of slow site speed, they may leave the website altogether, thus increasing the bounce rate.

This leads to the dilemma of designing a website with optimal load speed — without sacrificing the image quality. The best practices indicate using image optimisation to tweak a few aspects of the image before uploading it to a website.
Given the size of files, there’s often a necessity to compress the right file types for optimal website performance. However, optimising every image is time-consuming, so we thought of coming up with this guide to let you know if it’s essential to optimise images without sacrificing quality. Also, look for some of the nifty optimisation techniques for media files mentioned later.
So, without further ado, please take a look; let’s begin!
Want to receive updates? Sign up to our newsletter
Each time a new blog is posted, you’ll receive a notification, it’s really that simple.
What Is Image Optimisation?
The first step in optimising images for the web is grasping what the technique really involves. While it might sound straightforward, many find how it works a bit perplexing.
The aim of image optimisation is to reduce data and disc space usage while maintaining high-quality visuals on a web page. It involves shrinking file sizes without slowing down load times, ensuring images appear swiftly alongside text.
Using an automatic compression tool is one of the simplest methods to optimise images. These tools maintain image quality while reducing file size, boosting your site’s performance noticeably. There are, of course, other methods too, such as using a plugin, which can be just as straightforward.
Additionally, with more people browsing on smartphones, it’s crucial to modify pages and images like Google Photos to suit device capabilities, maintaining optimal performance.
Apart from the user-friendliness aspect of optimising images, ranking websites is also a powerful SEO technique. Image compression or optimisation has become indispensable for designing a high-performance website.
Benefits Of Image Optimisation
You may have heard from many people that optimising images is essential for maintaining a good web page. But what exactly are the benefits of spending hours on this extra step? Here, we will list some of the advantages of optimised images that you will notice soon after implementing the techniques for your web page.

1. Improved Page Load Speed
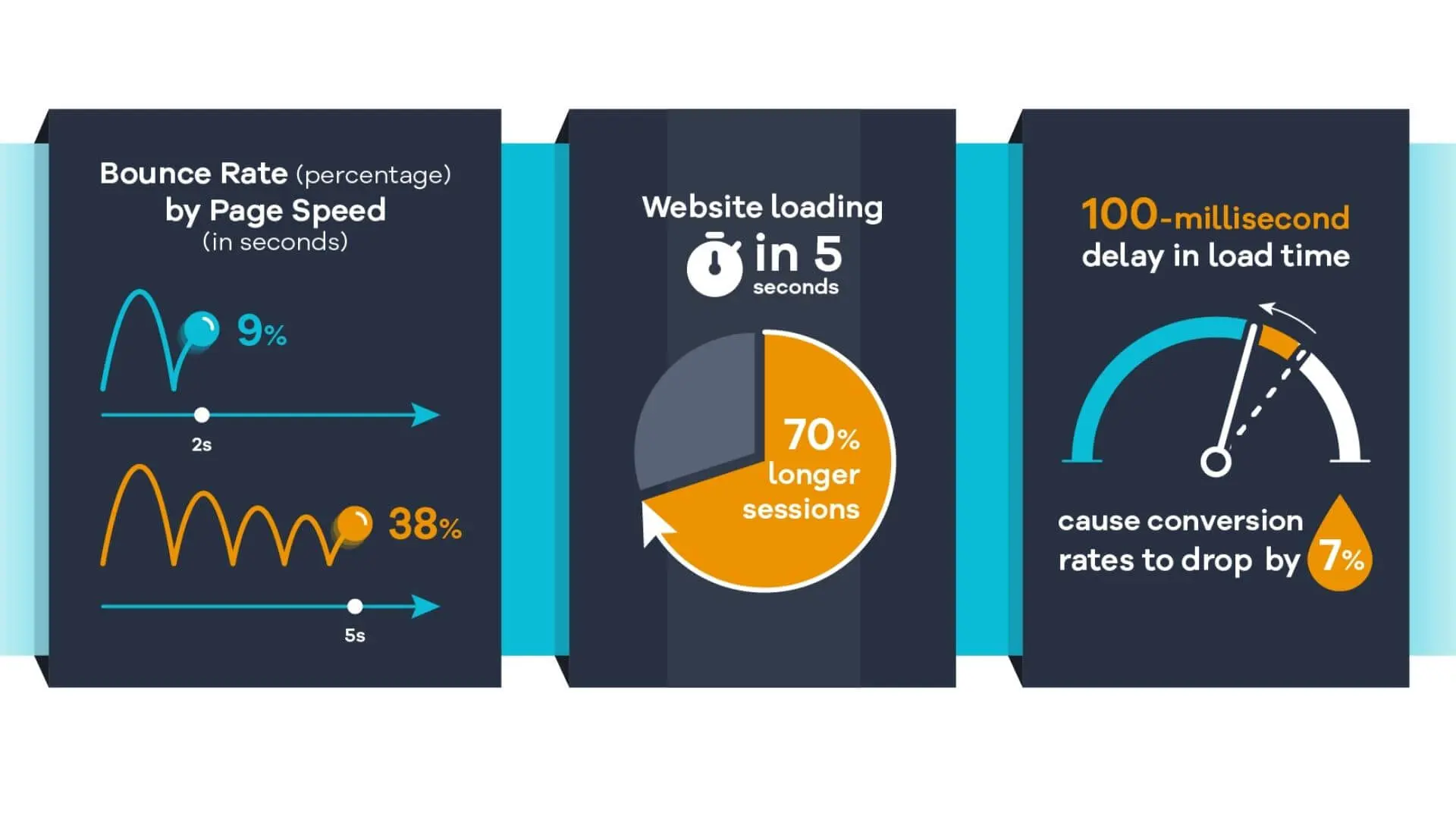
The foremost reason to alter image sizes is to improve the load time of a web page. Apart from your internet speed, the content of a page also matters when it comes to loading. However, it may also depend on design aspects, such as animated images, which can slow the load time.
To keep your audience engaged, make sure your web pages load in about two seconds by compressing images. Large images, especially from Google, can hog space, so optimising their size helps speed things up significantly.
This becomes especially true for mobile users who often switch between pages, ensuring quick page loads. So, when you optimise images for the web, it’s necessary to make changes for both PC and smartphone formats to ensure optimal user experiences.
While designing a website or uploading a new image online, check the existing loading speed and provide your email address for notifications on website performance. For instance, Google’s PageSpeed Insights is a favourite among developers as it gives a detailed look into how a website performs.
2. Enhance SEO Ranking
You may have already heard about the usefulness of SEO or search engine optimisation. It’s a technique to improve your website’s rank on search engines. However, no set parameters of SEO have been approved by a search engine to date.
So, most people need to experiment with different techniques to see if there are any changes, including handling larger file sizes. For instance, optimising the text with keywords and quality writing is a frequently used measure for achieving a better rank on search pages.
Additionally, optimising images for SEO works quite well. Even search engines like Google prefer sites with a fast load speed, as they are well-received by users.
So, even with great content and high-quality images on your web pages, lagging page load times may reduce the search page ranking. Thus, there’s no way to work past optimising the images for your website.
Apart from reducing the file size of an image, adding proper alt texts and titles to the image file may also help increase the searchability of an item. Your website’s images may even improve your page speed and appear in search results with the proper techniques.
Moreover, optimising images for a better ranking is especially important for those running e-commerce websites. These websites are often image-heavy, so the webpage load times tend to be higher. However, optimal load time will enhance site performance and may help you rank higher than your competitor.
A higher search page rank also helps build the trust of potential customers because of the perceived value and ensures the best image of your company is presented. Nevertheless, use a compression method to retain the image quality and follow the recommended image dimensions mentioned by Google.
3. Increased Conversion Rate
If you run a website that offers products or services, there’s a chance of experiencing a low conversion rate. But, as your main goal is to make a sale, retaining the audience and making them interact with the page is essential. Optimising the images can lead to better conversion, as it’s directly linked to SEO and user-friendliness.

When someone searches for a particular keyword, and your site reach a top result, the user will have a good impression of you.
On top of that, if the site has been delivering high-quality images with helpful information and content, they will likely become your customers. It may also lead to the user checking out other pages on the website, which brings down the bounce rate and may also improve the website’s ranking.
At first, you may doubt that compressing image sizes may give such benefits. And although we can’t guarantee overnight success, it is sure to improve user-friendliness considerably.
SEO experts have found that people are unlikely to revisit a site with a long webpage loading time. The audience usually expects a website to load in two to three seconds, which is nearly impossible without optimising the images.
4. Better User Experience And More Engagement
The ultimate reason for designing a good website is to attract and impress the target audience. Indeed, you don’t want to see a high bounce rate for your website, which is often the case for photos without optimisation that weighs down a web page.
Using image optimisation in the right way helps increase user experience, and more people are satisfied with your offer. Along with a good search rank, a quick load time is the best impression on a person, especially if you have an e-commerce website.
The aim of pulling in an audience is to make them interact with other pages on the website. And people tend to get quite frustrated when pages take longer to load. Also, while optimising, you need to ensure that the load time is fast for all kinds of devices — the most important being smartphones.
Besides, there are instances where not properly optimised images or putting the wrong image file size can cost you heavily if devices cannot load the images. This makes the users unhappy, hurts your site’s reputation, and the design may appear unprofessional.
Additionally, it’s likely that a person will interact even more with a website when it loads quickly, leading to more sales for e-commerce sites. As a result, satisfied customers will return to the same websites in future.
With content-based websites, well-optimised images improve readability, helping users see the whole page before losing interest. On the flip side, if the page loading time increases by even a couple of seconds, the bounce rate may double or triple. In this way, image optimisation is the definitive way to improve the user experience.
How To Optimise Images For The Web?
You know that it’s worth spending time optimising the images and reducing the file size of large images with a high resolution. That said, knowing about the options that make the task easier is essential.
Yes, you are likely to invest some time in photo optimisation, but using image optimisation plugins can streamline the process, save images more efficiently and yield increasingly better results. Here, we have gathered some methods you can use to optimise photos for the web.

1. Easy Image Compression
As a beginner, the easiest thing to do is visit a photo compression site to reduce the file size. Simply put, compression is a technique where the data of a file is reduced, maintaining a high-quality image without hampering the quality.
Several websites that compress images utilising different techniques are available but try to find one with a secure connection. You’ll need to upload the image on such websites and choose the desired amount of compression. You may even select a deduction in quality to a certain extent if the file size is too large or has a high resolution.
These websites let you download the file in any popular image file, after which you can upload it to your website. When it comes to the dimensions, try to keep it above 1200 pixels, the standard size preferred by Google.
2. Using Adobe Photoshop
I have experience designing websites, and you’ll surely know about the image editing software Adobe Photoshop. Most beginners find it convenient to reduce image size with the software.
Once you open Photoshop, an open-source tool, you can find the “image size” option under the “image” tab. It allows you to change the width and height of an image’s pixel or size and its resolution while maintaining a quality image. While saving an edited image, you can also use the “save for web” option to get a small image size with higher image quality.
Those already into image editing may also try tools like Affinity Photo, GIMP, and others to make the changes. Even simple editors, such as Microsoft Paint, can help reduce the file size for online images.
3. Lossy And Lossless Compression
Recently, the talking point of data compression has been about whether to use lossy or lossless compression. So, before you proceed to optimise web images, it’s good to know about these two popular ways of image compression.

A) Lossy Compression
To optimise your images using lossy compression, there are inexact approximations and discarding partial data to reduce the file size. However, this technique might have some quality loss, which may not be ideal for some people.
Certain image file types reduced with lossy compression cannot be reverted to their original form once data is discarded. This form of compression has a better data-holding capacity, which is excellent for compressing large image files.
B) Lossless Compression
As the name suggests, there’s no data loss in this technique. Hence, the format can be altered and reverted to its original form without losing quality.
But, when you resize your images, the file sizes are usually more manageable than in lossy compression. A file type like PNG images is a suitable example of lossless compression, and many people prefer this format on their websites.
It is worth noting that there isn’t any harm in either compression technique. However, it would help ensure the image file is tweaked to reduce the page loading time. So, now and then, you may need to settle for lossy compression to increase the speed but remember to still maintain a higher quality within your images.
But try to keep the compression level within 50% to avoid any noticeable quality changes that may affect the look of your website.
4. Choosing The Right Image File Format
The file formats you choose are intertwined with the application of either lossless or lossy compression techniques. That said, selecting the correct file type is essential to see the benefits of any image compression. Here are some of the standard file types or formats seen in images for web use:
A) JPEG
This is the most common file type seen on the internet that can be reduced considerably. You will usually end up with a JPEG file while downloading a picture from the web. It’s also the usual format in which a file is saved after lossy compression.
While JPEG files, optimised using a smart lossy compression technique, help decrease the page loading time, the important thing is to compress the JPEG images so that the loss of quality isn’t too evident.
B) PNG
Another predominant file image format is PNG, which is often used to retain the high-quality features of an image, especially graphics. A PNG file is solely reserved for web use and not for print.
As we said, compressing a file in the lossless technique usually converts a photo to the PNG format, resulting in a smaller file size. It’s also a usual choice for decorative images on a website. However, compared to a JPEG image, the image size is larger.
C) WebP
One of the latest image formats, WebP, is a file image format that works on Google Chrome and Firefox, two of the most widely used browsers.
WebP images are said to be smaller than JPEGs while retaining better quality. WebP supports transparency, so it has the edge over PNG when optimising images.
The only catch about using this file format for online use is the lack of support in Safari browsers. Simply put, Mac or iPhone users won’t be able to access WebP images.
D) GIF
Most people are aware of PNG GIF images because of their popularity in the context of online memes. But, when it comes to using this file type for web design, we suggest you choose the right options due to the small file size of GIF images.
E) AVIF
AVIF is a new technology getting widespread adoption by all modern web browsers and operating systems, and it’s derived from the keyframes of AV1 video. Its widespread adoption in modern browsers and devices makes it a perfect alternative to WebP; whilst it’s not supported in older browsers, a fallback option is possible. AVIF is a natural alternative to WebP with similar results in compression.
5. Naming The Image File
Have you ever noticed the file names of images using a specific software that come up after you save photos? If not, you should, as it’s usually something that’s attributed to the image by your camera. It can also be a generic file name given by the original file uploader of a site.
With that in mind, ensure that you alter the file name to accommodate the keywords in the content. Using descriptive image file names also helps web crawlers of Google identify the image and rank the website accordingly.
For instance, rather than using a generic keyword for the image, like “fountain-pen.jpg”, you can optimise images for the web and use specific keywords that go more in-depth, such as “vintage-1950-Conway-Stewart-388-fountain-pen.jpg”.
It’s essential to do so, as users often search using specific keywords, such as ’vintage Conway Stewart 388’. So, including the keyword may give them search results where your website is listed.
Some people like to dive deep into the keyword patterns of their audience while optimising the image file name. However, as a beginner, try to keep the terms descriptive to make it easier for Google and other search engines to pick them up when showing results.
You may also want to categorise the media library so there aren’t any mix-ups between similar photos and file names.
6. Proper SEO-friendly Alt Text
The alt text is one of the most neglected parts of an online image. As it isn’t visible to most users, some people forget to add the alt text. However, to optimise the image on a website, it’s crucial to provide explanatory alt text.
“Alt texts” stands for alternative texts, which help visually-impaired persons navigate a website. You can see the alt text on some web pages when the cursor hovers over an image. It’s also visible if there’s an error while loading the image.
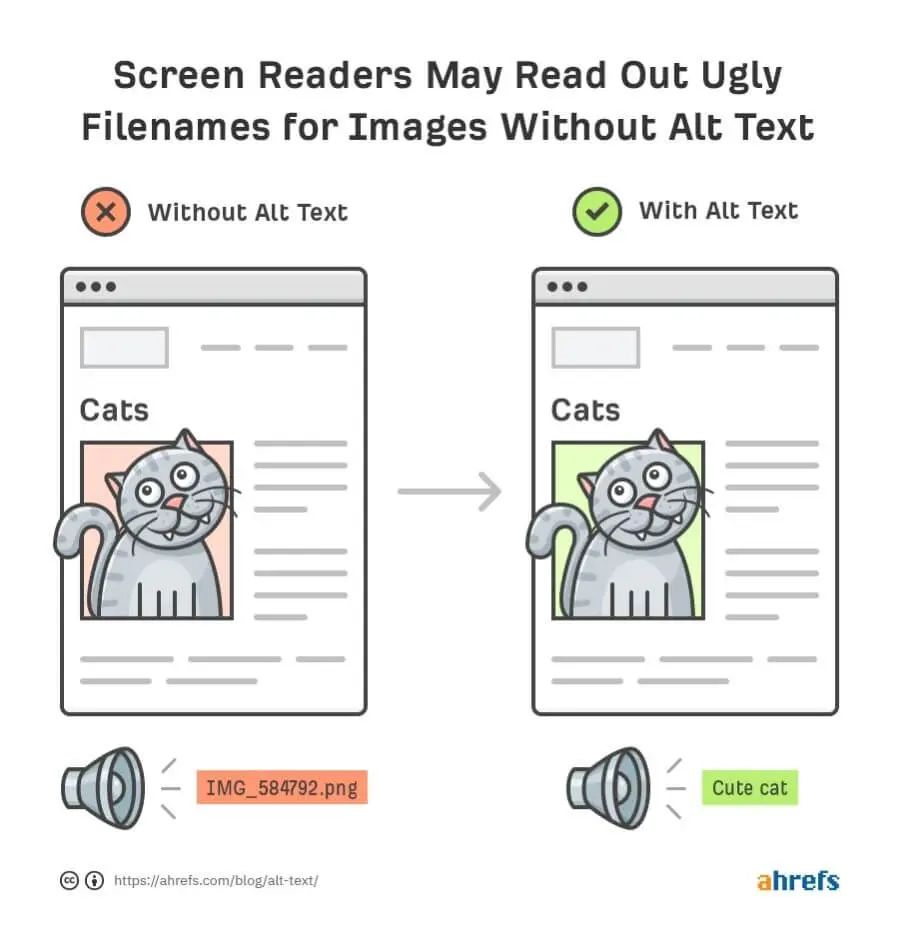
Apart from providing more accessibility, adding alt texts and attributes increases the chances of photos showing up in search engines. Alt texts add value to an image.
Also, remember that you must provide alt texts to all images on your website. Use plain and simple language to describe the image. For product images, try to use the serial number or model number along with the company name. So, something like “BIC push clip pen G55329” would work.
At the same time, a common mistake many people make is to stuff alt texts with keywords. It would be best not to do that, as Google may penalise the website for keyword stuffing. Also, remember not to use alt texts for decorative images as it may lead to over-optimisation, which is undesirable.
7. Using Plugins
If you’re using a content management platform like WordPress, you must consider using image optimisation tools or plugins to reduce file sizes after you upload images. As the plugins work automatically and optimise images, you don’t have to worry about selecting the dimension or size.
However, it is important to select a WordPress plugin that compresses the original image externally to prevent extended webpage loading times. Some options for such WordPress plugins include:
Optimising Images For Your Website
Hopefully, you know why tweaking images is integral to creating a user-friendly web page and proper SEO optimisation.
Of course, beginners may need some time to pick up all the techniques or figure out what kind of images make a significant impact and what form of optimisation works for their particular website. However, your time and effort will be rewarded with excellent loading speed and, perhaps, more audience interaction.
We hope our informative guide has helped you determine the benefits of image optimisation and how to get started. On that note, share your thoughts and experience with image optimisation in the comments section.




